Guide to Arrays in Delphi
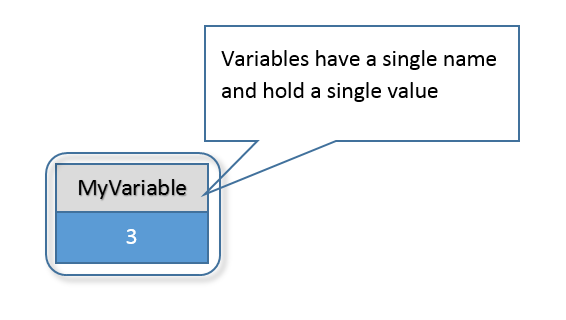
What is an Array?
How do I make one?
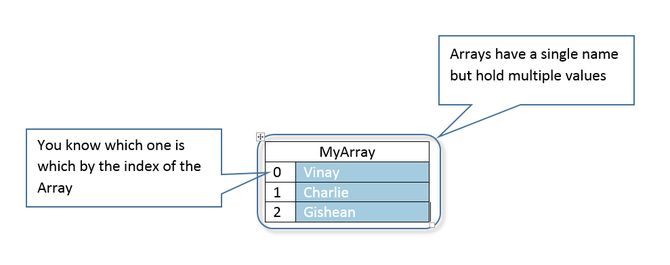
Create an array in Delph like this:
myArray : Array[0..2] of string;
Each 'box' in an array is called an element
The elements are referred to with the index
The numbers in the array definition above tell Delphi how many elements to create and where to start numbering them.
The elements are referred to with the index
The numbers in the array definition above tell Delphi how many elements to create and where to start numbering them.
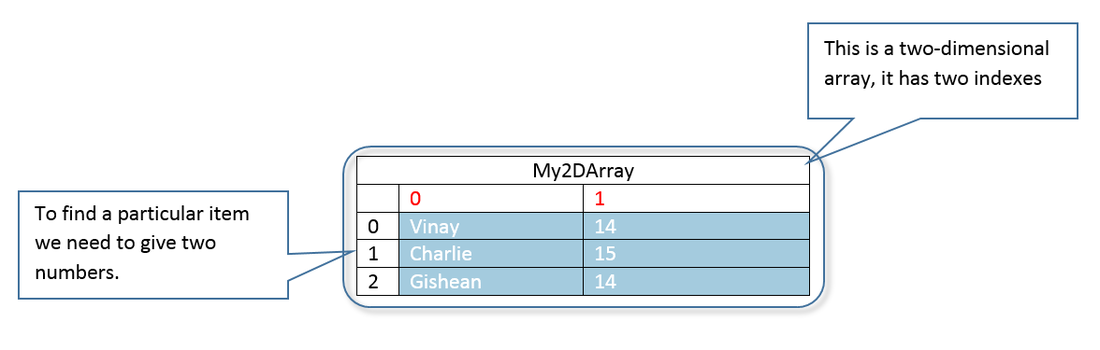
Two dimensional arrays
Two dimensional arrays are like tables. You can use them to store multiple items of data - for example multiple answers. To make one it's just the same as for a one dimensional array, except that you tell Delphi to give it two number ranges:
myArray : Array[0..2,0..1] of string;
Here we've said that there are three rows, numbered 0,1 and 2 - and two columns numbered 0 and 1. To find Gishean's age we indicate which array element we want like this;
myResult = myArray[2,1]
.. which says 'go to row with index number 2 and column with index number 1.